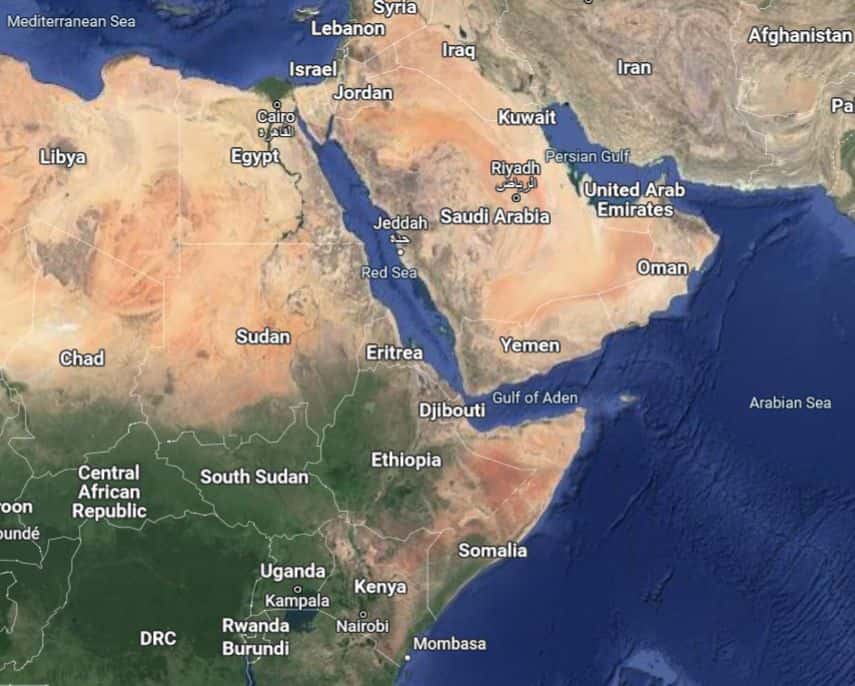
HORN OF AFRICA
The Horn of Africa, also known as the Somali Peninsula, refers to the easternmost region of Africa, comprising Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Broader definitions also include parts of Sudan, South Sudan, Kenya, and Uganda. It is located in close proximity to the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden.
The region is known for its diverse topography, including highlands, plateaus, and coastal areas. It has a unique cultural heritage and history, and it faces various challenges such as political conflicts, internal strife, and issues related to food security and development.
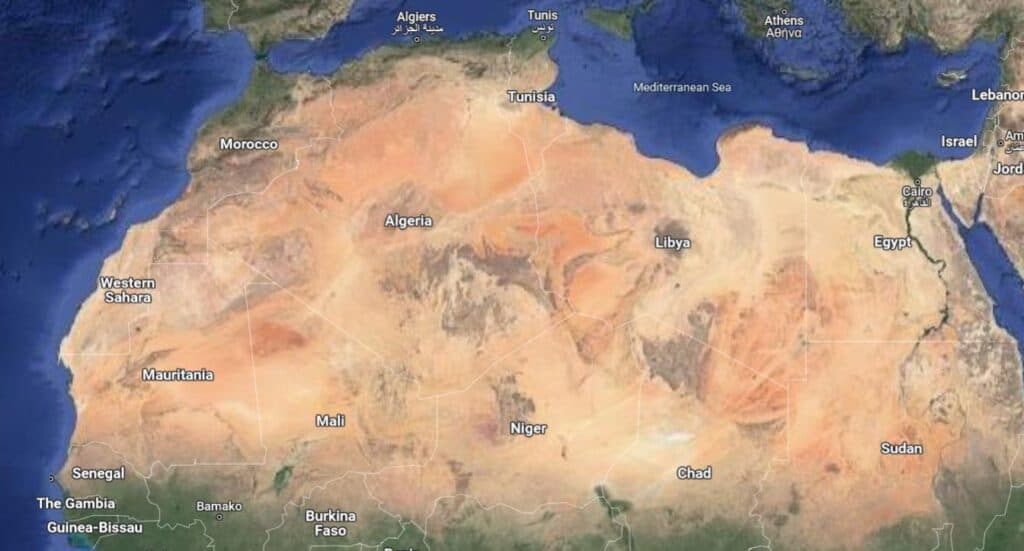
SAHARAN AFRICA
Saharan Africa refers to the region that encompasses countries located primarily within the Sahara Desert or heavily influenced by its geography.
It includes countries such as Algeria, Chad, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Sudan, and others. This region is characterized by its arid and desert landscapes, with limited access to water resources and challenging living conditions. The region is bordered in the west by the Atlantic Ocean, in the north by the Atlas Mountains and Mediterranean Sea, in the east by the Red Sea, and in the south by the Sahel.
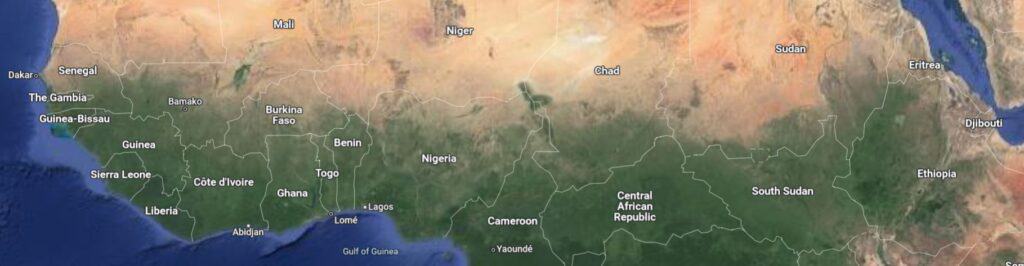
THE SAHEL
The Sahel is a transitional zone that spans across several countries in Africa, located immediately south of the Sahara Desert.
It stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east, covering – from west to east – countries such as parts of northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, the extreme south of Algeria, Niger, the extreme north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic (CAR), central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia.
The Sahel region is characterized by semi-arid conditions, with a mix of desert and savanna landscapes. It faces various challenges, including recurrent droughts, environmental degradation, and socioeconomic instability.
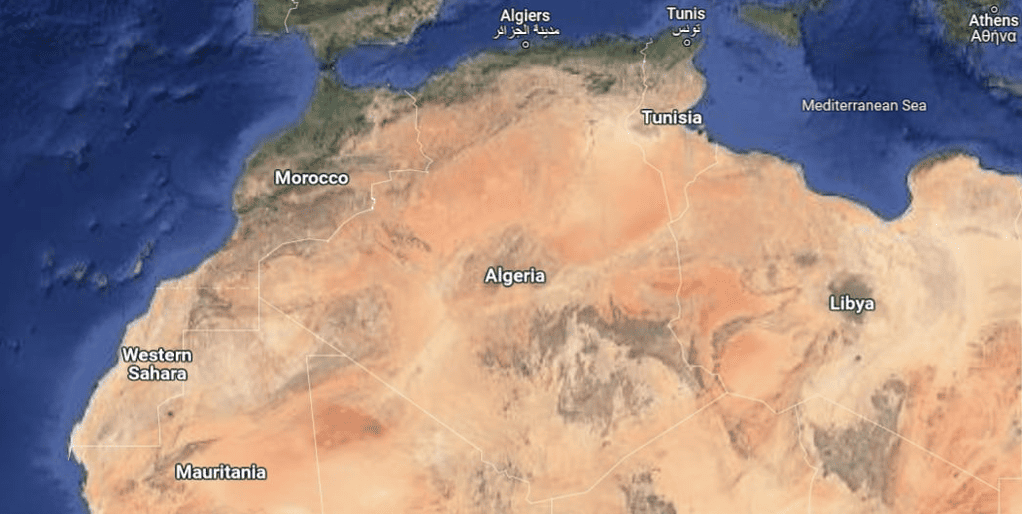
THE MAGHREB
The Maghreb is the western part of North Africa and the westernmost part of the Arab world. It includes the countries of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania, which lie along the Mediterranean coast to the Atlantic Ocean.
The dominant religion in the region is Islam, and it plays a significant role in the culture, traditions, and daily life of the people.
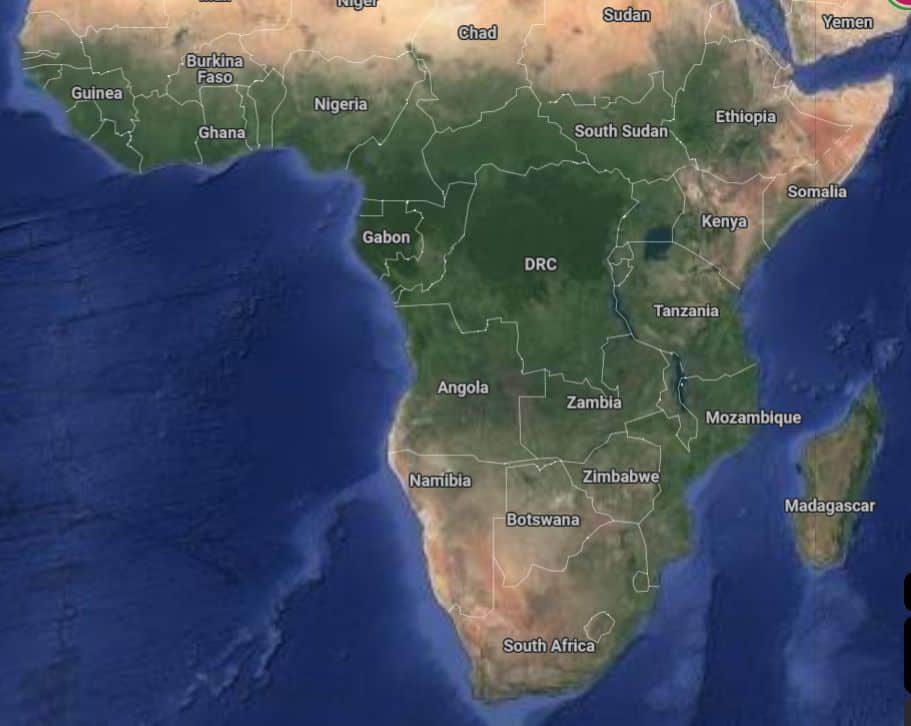
SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA
Sub-Saharan Africa refers to the region that spans the vast majority of the African continent, excluding the countries located within or heavily influenced by the Sahara Desert.
It includes countries from the southern fringes of the Sahara Desert downwards, encompassing the diverse landscapes, cultures, and peoples of Africa. Sub-Saharan Africa is known for its diverse ecosystems, including tropical rain forests, savannas, and grasslands. It is home to a significant portion of Africa’s population and is characterized by a range of economic, social, and political dynamics.
